Table of Contents
Sleep deprivation refers to the condition where an individual consistently fails to obtain the recommended amount of sleep needed for optimal functioning. While the ideal sleep duration may vary from person to person, most adults require around 7-9 hours of sleep per night. However, factors such as work demands, lifestyle choices, stress, and medical conditions can disrupt sleep patterns and result in sleep deprivation.
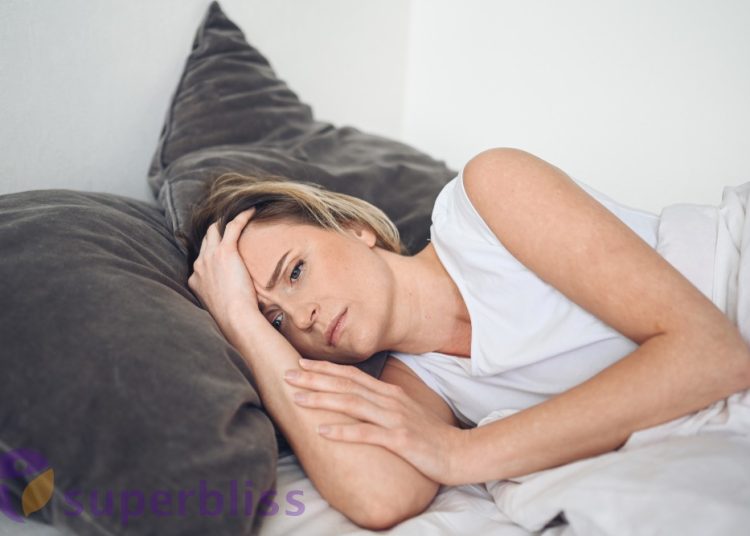

1 Impact on Physical Health
Sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on our physical well-being. Here are some ways it affects our bodies:
Weakened Immune System
Lack of adequate sleep weakens our immune system, making us more susceptible to illnesses such as the common cold, flu, and infections. Sleep deprivation impairs the production of immune cells and antibodies, compromising our body’s ability to fight off pathogens effectively.
Increased Risk of Chronic Conditions
Research has shown that sleep deprivation is linked to an increased risk of developing chronic health conditions. Conditions such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension have been associated with insufficient sleep. The disruption of hormone regulation caused by sleep deprivation can contribute to these health issues.
Weight Gain and Obesity
Sleep deprivation disrupts the balance of hormones that regulate appetite, resulting in increased hunger and cravings for high-calorie foods. Additionally, it can lead to reduced metabolism and impaired glucose tolerance, making weight gain and obesity more likely.
Impaired Physical Performance
Lack of sleep negatively impacts physical performance and athletic abilities. It reduces endurance, impairs coordination and motor skills, and slows down reaction times. Athletes and individuals involved in physically demanding activities are particularly vulnerable to the consequences of sleep deprivation.
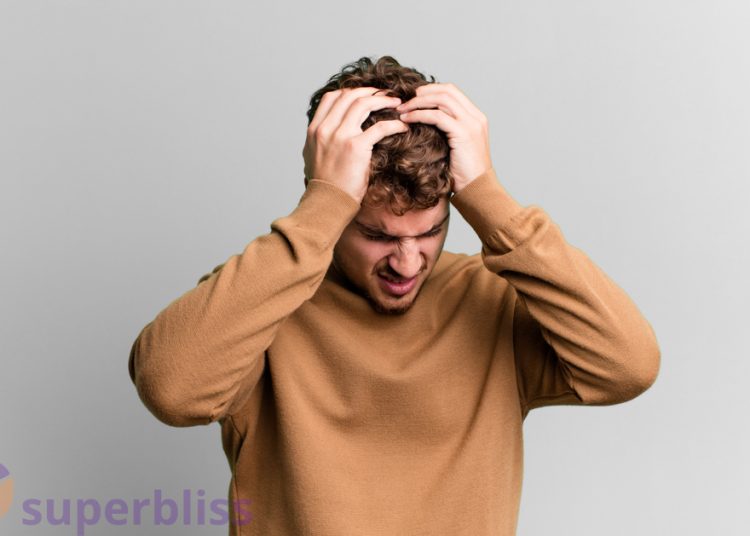

2 Impact on Mental Health
Sleep deprivation not only affects our physical health but also takes a toll on our mental well-being. Here are some ways it impacts our minds:
Cognitive Impairment and Lack of Focus
Inadequate sleep impairs cognitive function, including memory, attention, concentration, and problem-solving abilities. It becomes challenging to retain information, learn new things, and perform complex mental tasks. Sleep-deprived individuals often experience difficulties with decision-making and problem-solving due to reduced mental clarity and focus.
Emotional Instability and Mood Disorders
Sleep deprivation disrupts the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, leading to emotional instability and an increased risk of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. Irritability, mood swings, heightened emotional reactivity, and feelings of sadness or hopelessness are common among those suffering from sleep deprivation.
Increased Risk of Mental Health Disorders
Long-term sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of developing mental health disorders. Conditions such as depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia have been associated with chronic sleep deprivation. Adequate sleep is essential for maintaining optimal mental health and emotional well-being.
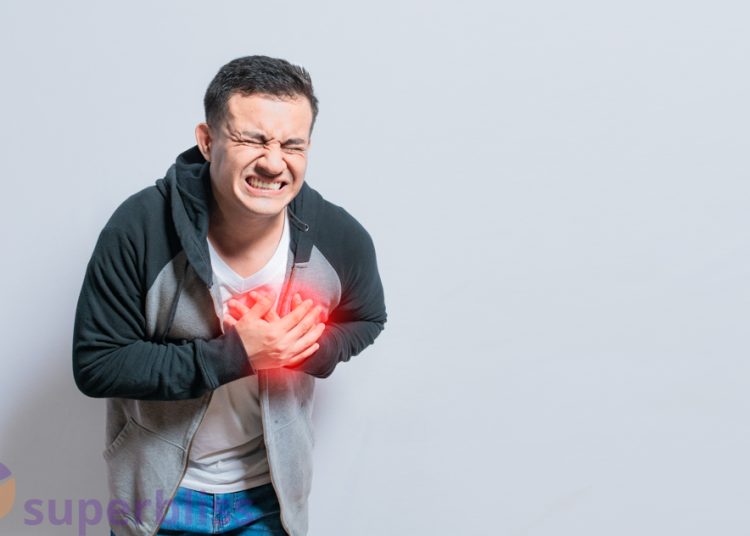

3 Relationship with Chronic Conditions
Sleep deprivation can contribute to the development or exacerbation of chronic conditions. The following are some examples of how inadequate sleep can impact specific health issues:
Cardiovascular Health
Sleep deprivation increases the risk of hypertension (high blood pressure), heart disease, and stroke. The disruption of the body’s natural processes during sleep can lead to elevated blood pressure levels and inflammation, contributing to cardiovascular problems.
Diabetes
Lack of quality sleep is associated with an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Sleep deprivation affects insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, leading to higher blood sugar levels and an elevated risk of insulin resistance.
Hormonal Imbalances
Sleep deprivation disrupts the production and regulation of hormones, such as cortisol, growth hormone, and leptin. These imbalances can contribute to weight gain, impaired metabolism, and increased stress levels.
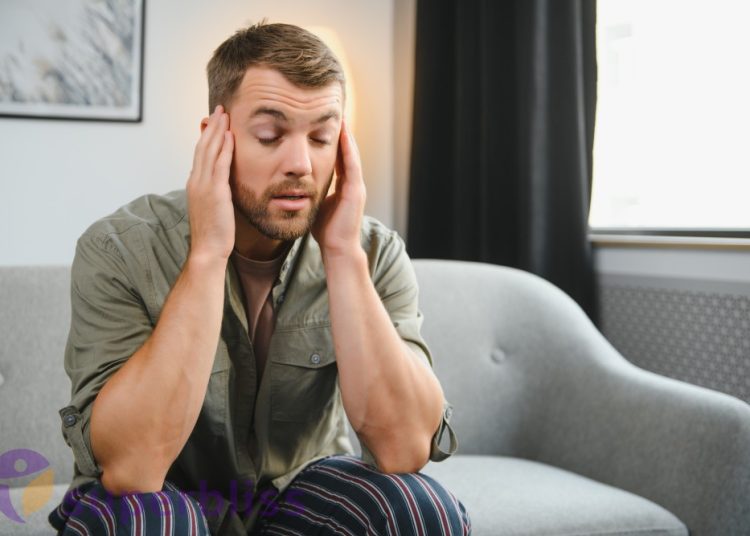

4 Cognitive Impairment and Lack of Focus
Sleep deprivation significantly impairs cognitive function and affects our ability to focus and concentrate. The following aspects highlight how inadequate sleep affects our mental performance:
Memory Consolidation
During sleep, our brains consolidate memories and information gathered throughout the day. Insufficient sleep disrupts this crucial process, leading to difficulties in retaining and recalling information. Adequate sleep enhances memory formation and promotes efficient learning.
Reduced Alertness and Attention
Sleep deprivation decreases alertness, making it challenging to stay focused and engaged in tasks. Attention span and reaction times are significantly compromised, affecting productivity and overall performance.
Impaired Decision-Making
Lack of sleep hampers our ability to make sound decisions. Sleep-deprived individuals often struggle with critical thinking, problem-solving, and evaluating different options. This can have implications in various aspects of life, including work, relationships, and personal goals.

5 Emotional Instability and Mood Disorders
Sleep deprivation has a profound impact on our emotional well-being and can contribute to the development of mood disorders. The following factors highlight the relationship between sleep deprivation and emotional instability:
Emotional Regulation
Adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining emotional stability and regulating our emotions effectively. Sleep-deprived individuals are more prone to emotional reactivity, irritability, and mood swings. This can strain relationships and impact overall quality of life.
Increased Risk of Depression and Anxiety
Chronic sleep deprivation is associated with an increased risk of developing depression and anxiety disorders. The lack of quality sleep disrupts neurotransmitter levels, such as serotonin and dopamine, which are vital for mood regulation.
Impaired Stress Management
Sleep deprivation reduces our ability to cope with stress effectively. It amplifies the physical and psychological responses to stressors, making it more challenging to manage daily pressures. This can lead to a vicious cycle where increased stress further disrupts sleep, exacerbating the negative impact on mental health.

6 Sleep Deprivation and Weight Gain
Inadequate sleep is closely linked to weight gain and obesity. The following factors explain this relationship:
Disrupted Hormonal Balance
Sleep deprivation disrupts the hormones that regulate appetite, namely ghrelin and leptin. Ghrelin, the “hunger hormone,” increases, leading to heightened appetite and cravings for unhealthy foods. At the same time, leptin, the hormone responsible for signaling fullness, decreases, making it challenging to recognize satiety.
Altered Metabolism
Sleep deprivation negatively impacts metabolic function. It reduces the body’s ability to process glucose effectively, leading to higher blood sugar levels and an increased risk of insulin resistance. Additionally, it can lower metabolic rate, making weight loss more difficult.
Increased Snacking and Poor Food Choices
When sleep-deprived, individuals often seek energy through unhealthy means, such as sugary snacks and caffeinated beverages. These choices provide temporary energy but contribute to weight gain over time. Moreover, impaired decision-making due to lack of sleep can lead to poor food choices and overeating.

7 Impaired Immune Function
Adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining a strong and healthy immune system. Here’s how sleep deprivation affects our immune function:
Reduced Immune Response
Sleep deprivation compromises the production of immune cells and antibodies needed to fight off infections and diseases. This weakened immune response makes individuals more susceptible to illnesses and infections.
Prolonged Recovery
When sleep-deprived, our bodies take longer to recover from illnesses and injuries. The immune system’s ability to heal and repair tissues is compromised, leading to prolonged recovery periods and increased vulnerability to further health complications.
Increased Inflammation
Chronic sleep deprivation can trigger a state of chronic low-grade inflammation in the body. Inflammation is linked to various health conditions, including autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular problems, and mental health disorders.

8 Increased Risk of Accidents
Sleep deprivation significantly impairs cognitive function, reaction times, and decision-making abilities, increasing the risk of accidents. The following scenarios highlight how lack of sleep can impact different areas of life:
Motor Vehicle Accidents
Drowsy driving is a serious concern associated with sleep deprivation. Fatigue impairs concentration, slows reaction times, and increases the likelihood of errors while driving. Falling asleep at the wheel or being inattentive can lead to severe accidents and injuries.
Workplace Accidents
Sleep-deprived individuals are more prone to workplace accidents due to decreased alertness and impaired focus. In industries where precision and quick reflexes are necessary, such as construction, manufacturing, or healthcare, the risk of accidents increases significantly.
Decreased Productivity and Performance
Sleep deprivation reduces productivity and hinders optimal performance in various areas, including work, academics, and daily tasks. Fatigue affects attention to detail, problem-solving abilities, and overall efficiency, leading to subpar results.
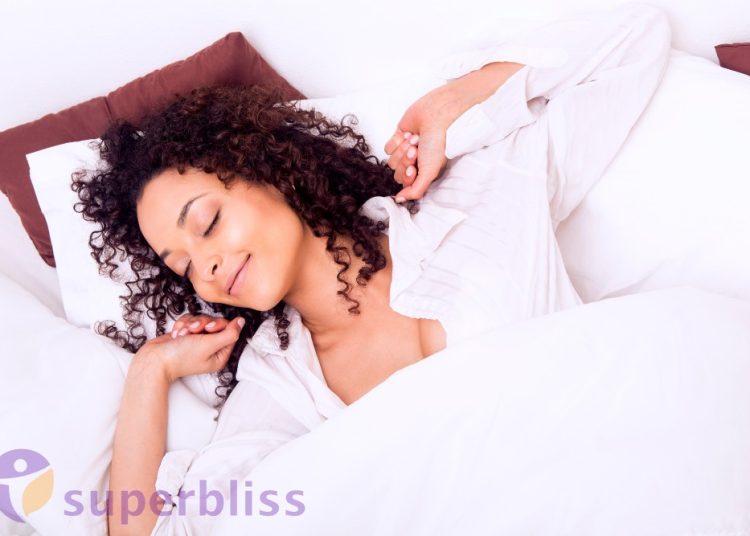

9 Strategies for Promoting Quality Sleep
To ensure adequate sleep and maintain optimal physical and mental health, it is essential to prioritize sleep hygiene and adopt healthy sleep habits. Here are some strategies to promote quality sleep:
- Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in calming activities before bed, such as reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques.
- Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Make sure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Use comfortable bedding and consider using white noise machines or earplugs if necessary.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed: Avoid electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, or laptops for at least an hour before bedtime. The blue light emitted by these devices can disrupt sleep patterns.
- Avoid Stimulants: Limit the consumption of caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol, as they can interfere with sleep quality and disrupt the sleep-wake cycle.
- Engage in Regular Exercise: Physical activity during the day promotes better sleep at night. However, avoid intense workouts close to bedtime, as they may increase alertness.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or journaling to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation.
- Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Invest in a supportive mattress, pillows, and bedding that suit your preferences and promote a restful sleep experience.
- Avoid Heavy Meals Before Bed: Opt for light, easily digestible snacks if you feel hungry before bed. Heavy meals can disrupt sleep and cause discomfort.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed: If you consistently struggle with sleep or suspect an underlying sleep disorder, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and guidance.
10 Bottom Line
Quality sleep is vital for maintaining optimal physical and mental health. Sleep deprivation can have profound consequences on our overall well-being, affecting both our bodies and minds. By understanding the impact of sleep deprivation, we can prioritize healthy sleep habits and seek necessary interventions to ensure restful and rejuvenating sleep.
11 FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How many hours of sleep do adults need?
Most adults require around 7-9 hours of sleep per night for optimal functioning.
Can sleep deprivation lead to weight gain?
Yes, sleep deprivation is linked to weight gain and an increased risk of obesity due to its impact on hormones that regulate appetite.
Is sleep deprivation reversible?
Yes, by adopting healthy sleep habits and prioritizing quality sleep, individuals can reverse the effects of sleep deprivation and improve their overall well-being.
How does sleep deprivation affect academic performance?
Lack of sleep impairs cognitive function, memory, and concentration, which can negatively impact academic performance.
Can napping compensate for sleep deprivation?
While short power naps can provide a temporary boost in alertness, they cannot fully compensate for the negative effects of chronic sleep deprivation. Establishing a regular sleep schedule is essential for long-term well-being.
Note: The above content is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making any dietary or lifestyle changes.


 Fitness
Fitness




 Weight Loss
Weight Loss




 Health
Health

 Popular Items
Popular Items Health Recipes
Health Recipes




 Health Tools
Health Tools Media Feeds
Media Feeds



 Discover:
Discover: 










Discussion about this post